OSI Model¶
The Open Systems Interconnect model is a conceptual framework for understanding the various layers of abstraction involved in networked communication.
Layer 2 Protocols¶
Data Link Layer
LLDP¶
ARP¶
The Address Resolution Protocol allows computers within a switched network to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses. This is done by simply broadcasting a request on the subnet that asks who owns a particular IP address. A response will arrive that contains the MAC address of the interface that is configured to listen to that address. It is certainly possible for multiple devices to respond to the same IP address, although this typically is not desired for obvious reasons.(1)
- In cases like where you configure a VIP (meaning, two devices are configured for the same IP address), only one of the devices would typically be "active" and respond to such requests. The VIP active/passive configuration is controlled by device-side applications like VRRP.
Layer 3 Protocols¶
Network Layer
ICMP¶
Internet Control Message Protocol is used to diagnose issues in a network. The traceroute and ping commands use ICMP.
Layer 4 Protocols¶
Transport Layer
QUIC¶
QUIC is a transport-layer protocol that aims to be effectively equivalent to TCP but with much reduced latency. This is achieved primarily through an abbreviated handshake protocol that only requires 1 round trip, whereas TCP requires 3. It can be thought of as a TCP-like protocol with the efficiencies of UDP.
Congestion control algorithms are handled in userspace instead of kernel space (like TCP) which is claimed to allow the algorithms to rapidly evolve and improve.
TCP¶
UDP¶
Layer 7 Protocols¶
HTTP¶
Obviously this has to be mentioned. It's the most common protocol of them all!
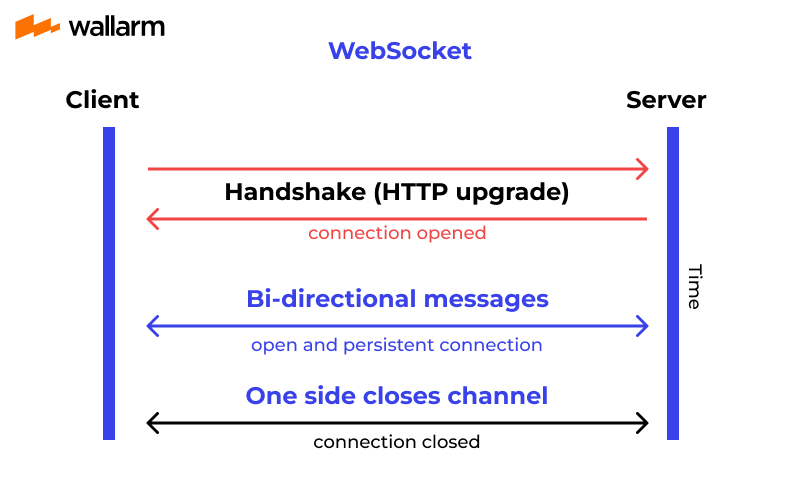
Websocket¶
gRPC¶
Google Remote Procedure Call.
Video Streaming¶
There are various standardized protocols for video streaming.
MPEG-DASH¶
MPEG stands for "Moving Picture Experts Group." DASH stands for "Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP". This protocol is used by YouTube and Netflix.
Apple HLS¶
HLS stands for "HTTP Live Streaming"
Microsoft Smooth Streaming¶
Seems to be exclusively used by Microsoft's products
Adobe HTTP Dynamic Streaming (HDS)¶
Mainly used for flash.